

With these libraries, you are ready to capture and process the traffic flowing in your LAN.
#Debian install tcpdump drivers#
Tstat requires, by itself, a few library that should already be installed on your system, such as libpcap (available from ) and the DAG drivers (available from ), in case you use such hardware. If you are able to run Tstat on other OSes, we'll be happy to include them in the list. It should work under FreeBSD, NetBSD, and other unix-like systems, (although we don't have any of those platforms for testing purposes).

It includes support for compilation for Android, and has been reported working on OpenWRT.
#Debian install tcpdump mac os x#
Tstat is tested on Linux systems (currently Ubuntu, Debian, RedHat, and CentOS, using 2.x and 3.x kernels), and on Mac OS X (starting from 10.6 Snow Leopard to the current 10.10 Yosemite). A more general description of the program as well as other documentation can be found in the Tstat homepage Requirements Operating System This document provides basic information for the installation, configuration and usage of Tstat and the Bayesian framework for Skype traffic identification.

Win 63000 - The window number (bytes in receiving buffer). IP 143.110.237.64.22 - IP and port number of the source host.ħ0.112.17 - IP and port number of the destination host.įlags - TCP flags (SYN, ACK, PSH, etc).
#Debian install tcpdump how to#
Here’s how to interpret that line of data:Ģ3:36:59.581280 - Timestamp of when the packet was captured. To read pcap files, you will need tcpick or tcpxtractor wiresharkĮach packet that tcpdump captures is written as an individual line. To open the file for later analysis, use the -r option and the name of your file. pcap file extension, and can’t be read by an ordinary text editor. If you would rather save the network traffic output to file, instead of having it listed on your screen, you can always redirect the tcpdump output with the usual > and > operators.Īnother option is to write the network capture to file. This will display all network addresses as IP addresses, rather than resolving them to domain names.
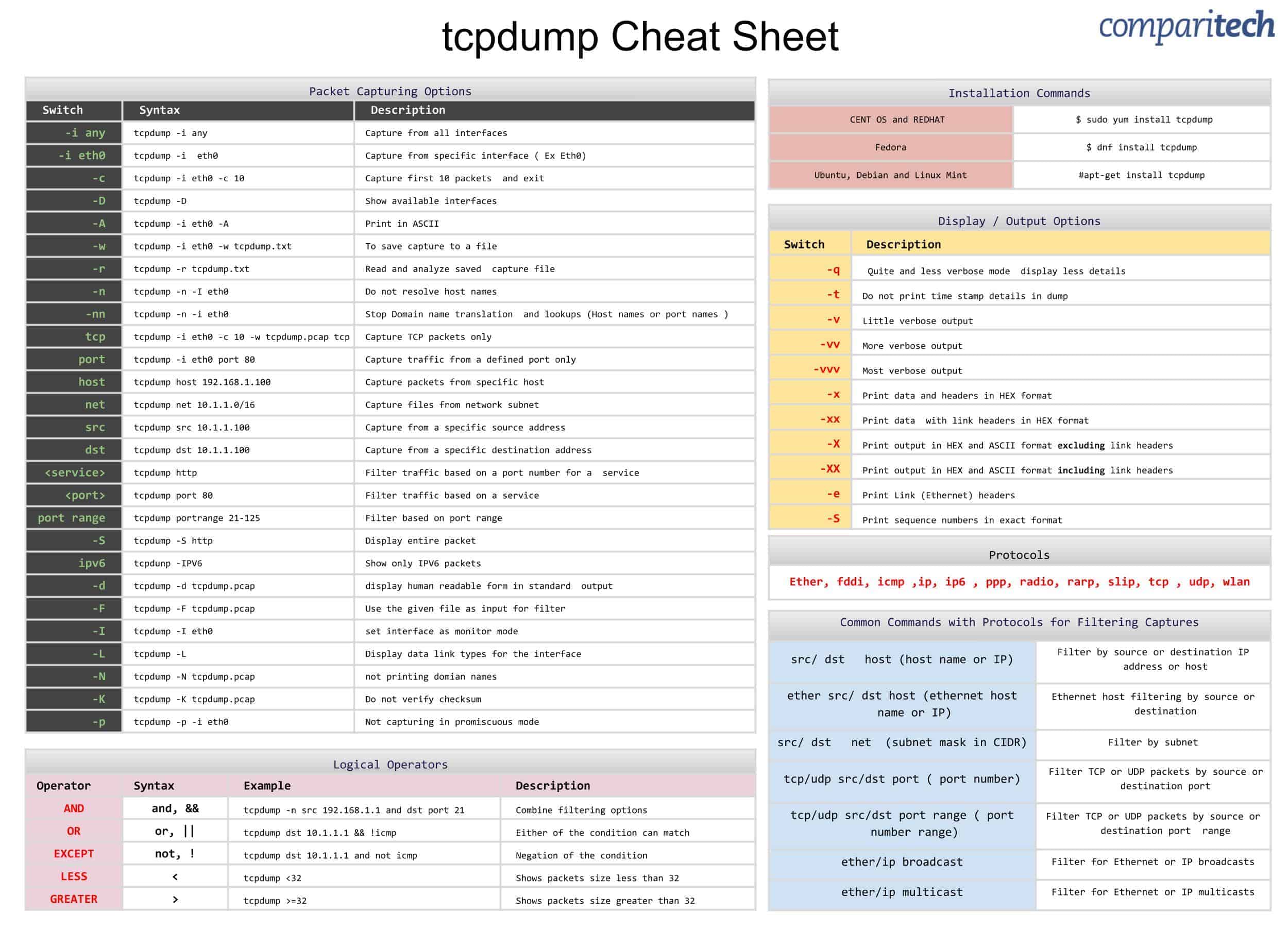
If you don’t want tcpdump to perform DNS resolution on the network addresses in the output, you can use the -n option in your command. The following command will allow us to capture only the first 15 packets. tcpdump will quit executing the command after the threshold has been reached, rather than waiting for you to interrupt. If you don’t want tcpdump to endlessly output data to your terminal, you can use the -c option to specify how many packets you’d like the utility to capture. You can use the -v option to increase the verbosity of the output, or -vv and -vvv to increase it even further. 3.any (Pseudo-device that captures on all interfaces) ĥ.nflog (Linux netfilter log (NFLOG) interface)Ħ.nfqueue (Linux netfilter queue (NFQUEUE) interface)Ĭapture packets from a particular ethernet interface using


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
